Intensive Care Unit (ICU)
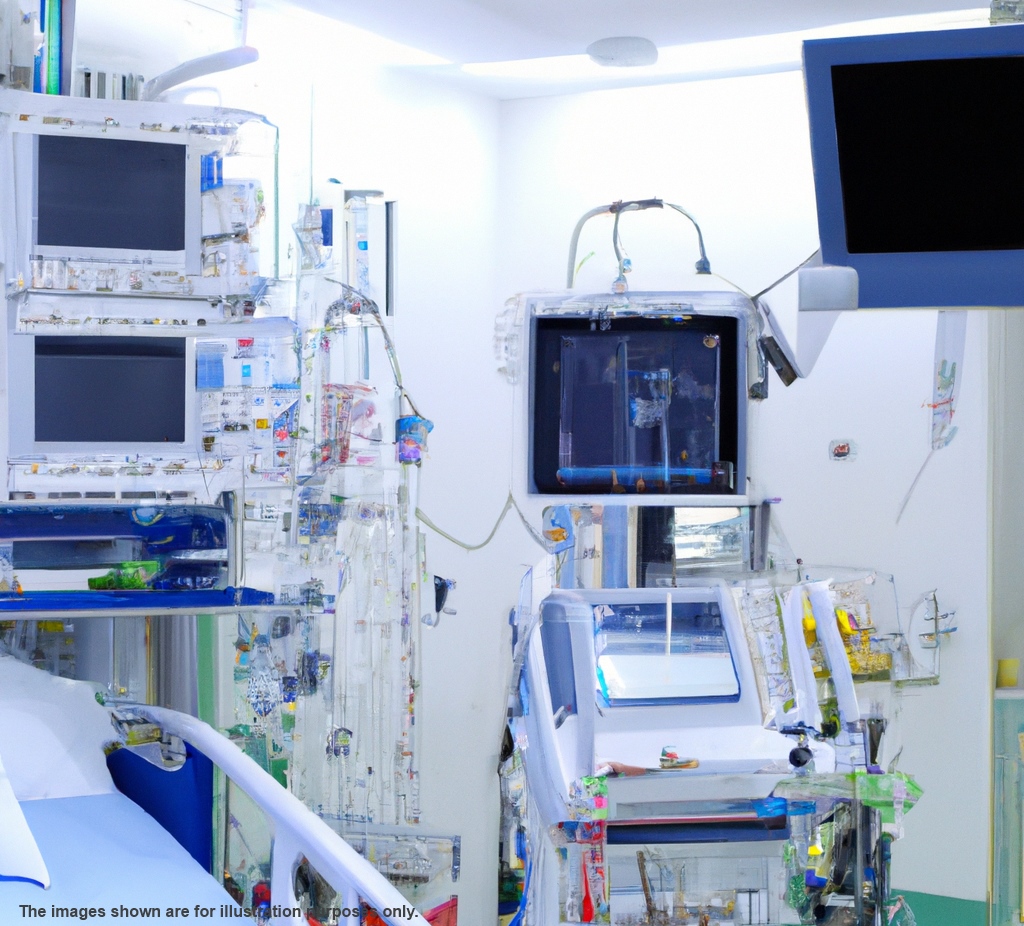
An Intensive Care Unit (ICU), Critical Care Unit (CCU), Intensive Therapy
Unit, or Intensive Treatment Unit (ITU) is a highly specialized department
within a hospital dedicated to providing intensive-care medicine.
ICUs are designed to oversee patients facing life-threatening conditions,
necessitating continuous, meticulous monitoring and support from advanced
equipment and medication to sustain normal bodily functions.
They boast heightened levels of staffing, specialized monitoring, and
treatment equipment, overseen by a team of physicians and critical care
nurses adept in managing the most critically ill patients.
Hospitals may house ICUs tailored to specific medical specialties or patient
groups, including:
- Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU)
- Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (PICU)
- Psychiatric Intensive Care Unit
(PICU)
- Coronary Care Unit (CCU), also known as
Cardiac Intensive Care Unit (CICU)
- Post Anesthesia Care Unit (PACU), also
referred to as the Post-Operative Recovery Unit
- High Dependency Unit (HDU)
Common ICU equipment encompasses mechanical ventilators to aid breathing
through an endotracheal tube or tracheotomy, cardiac monitors (including
telemetry), external pacemakers, defibrillators, renal dialysis equipment,
and instruments for continuous bodily function monitoring.
Additionally, a range of medical devices such as intravenous lines, feeding
tubes, nasogastric tubes, suction pumps, drains, and catheters are employed
alongside various drugs to address the primary conditions necessitating
hospitalization. Medical interventions such as induced comas, analgesics,
and sedation are frequently utilized in ICUs to manage pain and prevent
secondary infections.
Research suggests a correlation between ICU volume and the quality of care
for mechanically ventilated patients. Following adjustments for illness
severity, demographic factors, and ICU characteristics (including
intensivist staffing), higher levels of ICU staffing correlate significantly
with reduced ICU and hospital mortality rates.
Recommended nurse-to-patient ratios vary by country, with ratios of 2:1
commonly recommended for medical ICUs. However, staffing ratios differ; for
example, in Australia and the United Kingdom, most ICUs operate with
staffing ratios of 2:1 for High-Dependency patients requiring closer
monitoring or more intensive treatment than standard hospital wards, or even
1:1 for patients needing extremely intensive support and monitoring, such as
those on mechanical ventilation with concurrent anesthesia or sedation and
administration of potent analgesics.
folder_open General Hospital Information