Surgical Lighting
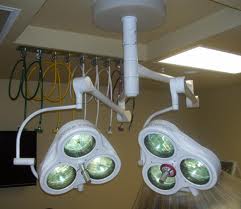
A surgical light, also known as an operating light or surgical lighthead, is
utilized by medical personnel to illuminate a specific area or cavity of a
patient during a surgical procedure. A combination of multiple surgical
lights is often referred to as a "surgical light system."
In the mid-1850s, surgical operations relied heavily on natural sunlight,
with operating rooms constructed facing southeast and equipped with ceiling
windows to maximize sunlight exposure. However, this method posed challenges
as surgical procedures were dependent on the time of day and weather
conditions. Additionally, there were issues with the illuminated area being
obstructed by medical personnel or equipment.
Attempts were made to address these challenges by installing mirrors on the
ceiling corners to reflect sunlight onto the operating table, but these
efforts only marginally reduced the issues. The use of optical condensers in
indirect lighting was also experimented with to minimize heat, albeit
without much success.
The introduction of electric lights in the operating room in the 1880s
presented new challenges due to the limited ability to control the emitted
light and the high levels of heat radiation.
With the advent of light-emitting diodes (LEDs) as light sources, the
problem of heat radiation was mitigated, and energy consumption reduced.
Terminology and Measurements:
- Lux (lx): Unit for measuring the amount of visible light at a specific
point, measured by a luxmeter.
- Central illuminance (Ec): The illuminance (in lux) at a distance of 1
meter from the light-emitting surface in the center of the light field.
- Light field center: The point in the illuminated area where the
illuminance reaches its maximum intensity, serving as the reference point
for most measurements.
- Depth of illumination: The distance beneath the light-emitting area where
the illuminance reaches 20% of the central illuminance.
- Shadow dilution: The ability of the light to minimize the effect of
obstructions.
- Light field diameter (D10): The diameter of the light field around the
center, where the illuminance drops to 10% of Ec, averaged from four
different cross-sections through the center.
- D50: The diameter of the light field around the center, where the
illuminance drops to 50% of Ec, averaged from four different cross-sections
through the center.
undo Medical Equipment